

The method of calculations of multiplication factors was developed in the early years of nuclear energy. It is necessary to define the infinite and finite multiplication factors of a reactor to describe the multiplication system. Some neutrons will cause further fission reaction, some will be captured by fuel or non-fuel materials, and some will leak out of the system. There is always a competition for the fission neutrons in the multiplication environment. It is necessary to decrease the non-fission neutron absorption in the system (e.g., to withdraw control rods) to sustain the chain reaction. On the other hand, if one neutron causes less than one further fission, the number of neutrons in the multiplication system will decrease in time, and the reactor power (reaction rate) will also decrease in time. The nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions. Moreover, this multiplication environment ( the nuclear reactor) behaves like an exponential system, which means the power increase is not linear, but it is exponential. To stabilize such a multiplication environment, it is necessary to increase the non-fission neutron absorption in the system (e.g., to insert control rods). In that case, the number of neutrons in the multiplication system will increase in time, and the reactor power ( reaction rate) will also increase in time. Suppose one neutron causes two further fissions. The chain reaction can take place only in the proper multiplication environment and only under proper conditions. This sequence of fission events is known as the fission chain reaction, and it is important in nuclear reactor physics.
Nuclear fission meaning free#
The fission process may produce 2, 3, or more free neutrons that are capable of inducing further fissions and so on. One class of nuclear weapon is the hydrogen bomb, which uses a fission reaction to "trigger" a fusion reaction.A nuclear fission chain reaction is a self-propagating sequence of fission reactions in which neutrons released in fission produce additional fission in at least one other nucleus. One class of nuclear weapon is a fission bomb, also known as an atomic bomb or atom bomb. The energy released by fusion is three to four times greater than the energy released by fission.


The energy released by fission is a million times greater than that released in chemical reactions but lower than the energy released by nuclear fusion. Takes little energy to split two atoms in a fission reaction.Įxtremely high energy is required to bring two or more protons close enough that nuclear forces overcome their electrostatic repulsion.
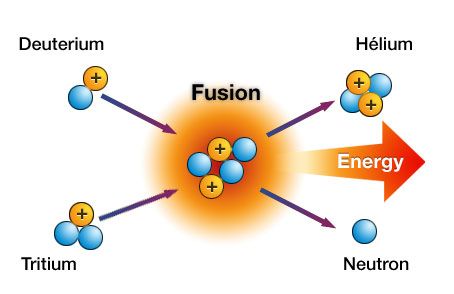
High density, high temperature environment is required. The main difference between these two processes is that fission is the splitting of an atom into two or more smaller ones while fusion is the fusing of two or more smaller atoms into a larger one.įission is the splitting of a large atom into two or more smaller ones.įusion is the fusing of two or more lighter atoms into a larger one.įission reaction does not normally occur in nature.įission produces many highly radioactive particles.įew radioactive particles are produced by fusion reaction, but if a fission "trigger" is used, radioactive particles will result from that.Ĭritical mass of the substance and high-speed neutrons are required. Nuclear fusion and nuclear fission are two different types of energy-releasing reactions in which energy is released from high-powered atomic bonds between the particles within the nucleus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
